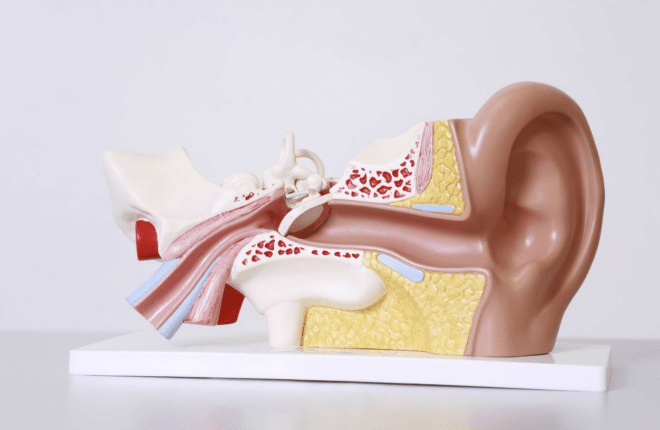
The Most Common Causes of Ear Pain
Ear pain is a ubiquitous yet distressing ailment that can be particularly alarming, especially for parents of young children. Understanding the causes of earaches can help individuals tackle the issue effectively, whether it’s through home remedies or professional intervention. This comprehensive guide explores the common triggers of ear pain, offers insights into the symptoms, provides self-care tips, and explains when you should consider seeking medical attention. Let’s take a closer listen to what your ear pain might be telling you.
Prevent Further Complications By Addressing Ear Pain Early
When the delicate structures of the ears are disrupted, pain is often the body’s way of signaling an issue that needs attention. Promptly addressing ear pain can prevent further complications and provide the relief needed to improve one’s daily functioning. Among the numerous conditions that can lead to ear discomfort, some are more frequent culprits. Uncovering the root of your ear pain is the first step toward a solution that allows you to hear and feel better. Below are the most common circumstances that result in ear pain.
- Ear Infections
An ear infection is the most notorious cause of ear pain, particularly in children. Whether it’s otitis external (infection of the outer ear), otitis media (middle ear infection), or otitis internal (inner ear infection), the throbbing or severe pain can be accompanied by fever, muffled hearing, and sometimes even the discharge of fluid from the ear. Ear infections often result from colds or allergies and can occasionally clear up on their own. If symptoms persist, you or your child may require antibiotic treatment. - Sinus Infections
Issues in the sinuses can indirectly affect the ears, leading to pressure and pain often mistaken for an ear infection. Sinusitis, or a sinus infection, can create inflammation in the nasal passages that block the Eustachian tubes – the passageways that connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. When these tubes are obstructed, they can trap fluid, lead to discomfort, and even impair your hearing. - Earwax Buildup
The body naturally produces cerumen – commonly known as earwax – to protect the ears from dust and particles. Under usual circumstances, earwax will slowly move from the eardrum to the ear opening, where it dries up and falls out. Some individuals may experience a buildup of wax that can result in ear pain, itching, a feeling of fullness, or tinnitus (ringing in the ears). While it’s important to note that cotton swabs are not the way to clean ears, softening with warm oil or over-the-counter eardrops and flushing them with water can relieve mild cases. - Foreign Objects in the Ear
Ear pain caused by a foreign object in the ear is common in children but can also occur in adults. Experiencing ear pain along with the sensation of something stuck in the ear suggests this might be the culprit. With children, it’s critical not to try removing the object without professional assistance, as it can push the object further into the ear. For adults, if the foreign object is visible and easy to grasp, it can be gently removed, but avoid pushing the object in deeper. - Swimmer’s Ear
Swimmer’s ear – medically termed otitis external – is an infection of the ear canal often caused by water remaining in the ear after swimming. Symptoms include pain, swelling, inflammation, and sometimes a yellowish discharge. Properly drying ears after swimming and using alcohol-based eardrops can help prevent this type of earache. - Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder
The temporomandibular joint is located in front of each ear and connects the jawbone to the skull. A disorder of this joint, often associated with a misalignment of the teeth or jaw, can cause pain that radiates to the ear. People with TMJ disorders may experience difficulty chewing, facial pain, and a clicking or popping sound in the joint. Treatment for TMJ disorders varies, from home remedies to dental or medical interventions. - Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
Your ears, nose, and throat are all connected, which is why dysfunction in the Eustachian tubes can lead to ear pain. When the tubes don’t open or close properly, perhaps due to allergies or a cold, air pressure in the middle ear can’t be equilibrated, causing pain. You might hear crackling or popping sounds and feel like your hearing is slightly muffled. Chewing gum, yawning, or the Valsalva maneuver can help relieve discomfort by opening the Eustachian tube.
Home Remedies for Ear Pain Relief
Whether you’re dealing with discomfort after a day of swimming or nagging pain from sinus pressure, there are immediate steps you can take to ease ear pain at home. These remedies are designed to provide quick relief for acute discomfort and should be employed as soon as symptoms emerge. From safe ways to deal with earwax to gentle methods to alleviate infection symptoms, let’s explore practical solutions you can apply right where you are.
Warm Compress
A warm compress applied to the affected ear can help soothe pain by improving blood circulation. Be cautious not to use excessive heat, which could lead to burns. A warm, damp towel is a simple and effective way to create a compress.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Nonprescription pain medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or acetaminophen (Tylenol), can help reduce pain and inflammation. Follow the dosage instructions and consult a healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
Saline Solution
A saline solution can provide gentle relief for inflammation in the inner ear. This simple mixture can be applied using a nasal spray bottle by tilting the head and providing a few spritzes or inhaling through the nose and discharging out the mouth.
Nasal Decongestants
If your earache is due to sinus congestion, over-the-counter nasal decongestants can help alleviate pressure. However, nasal sprays should be used for short periods as long-term use can have adverse effects, causing a condition called rhinitis medicamentosa.
Avoiding Irritants and Allergens
Steer clear of smoke, pollen, and other allergens that can exacerbate ear pain. Reducing exposure to these irritants can help your ears, especially if related to sinus pressure or allergies.
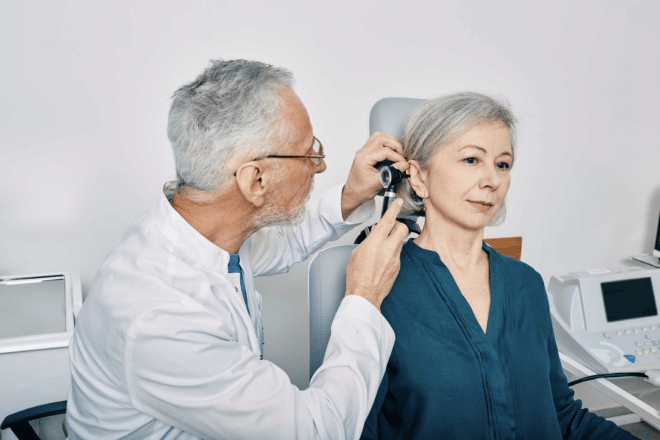
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many instances of ear pain can be resolved at home, some situations warrant a visit to a healthcare professional. When in doubt, it’s best to get checked out. Ear pain can be a sign of a serious issue, and timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial for your health. Seek timely medical attention if your or your child’s ear pain doesn’t improve within 24 to 48 hours. If it’s severe and accompanied by a high fever, significant hearing loss, or any drainage from the ear, the problem requires prompt evaluation by a doctor.
Remember, taking steps to manage ear pain swiftly at home can offer relief, but don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for persistent or severe symptoms. Your ears are key to your overall well-being, so give them the care they deserve.